Difference between revisions of "Mensuration"
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
# The students learn that mensuration is the branch of Mathematics dealing with measurement of angles, length, area, and volume. | # The students learn that mensuration is the branch of Mathematics dealing with measurement of angles, length, area, and volume. | ||
# Students will learn and understand that it is important to know how to measure things. | # Students will learn and understand that it is important to know how to measure things. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# The length of the total boundary of a figure is called its perimeter. The Metric unit of perimeter is same as the unit of length - Metre. | # The length of the total boundary of a figure is called its perimeter. The Metric unit of perimeter is same as the unit of length - Metre. | ||
# The perimeter of 2D geometrical figures like quadrilaterals can be obtained by calculating the sum of all the sides of the figure. | # The perimeter of 2D geometrical figures like quadrilaterals can be obtained by calculating the sum of all the sides of the figure. | ||
# The amount of surface covered by an object is called it area. The Metric unit of area is square metre. | # The amount of surface covered by an object is called it area. The Metric unit of area is square metre. | ||
# The capacity of an object to hold is called its volume. | # The capacity of an object to hold is called its volume. | ||
| − | |||
# They should develop the ability to calculate the area, perimeter, volume or side of many different figures. | # They should develop the ability to calculate the area, perimeter, volume or side of many different figures. | ||
| Line 71: | Line 68: | ||
# Why measure ? | # Why measure ? | ||
# How do we measure ? | # How do we measure ? | ||
| + | # What are the measuring modes and units seen at the market, Hospital, Chemist laboratories, Gold shop, Tailors, Bakeries, Petrol bunks, water tankers, milk vendors, contractors, kitchen, airport, and so on.? | ||
*Evaluation: | *Evaluation: | ||
| − | # | + | # Why do you think certain measuring standards are needed ? |
*Question Corner: | *Question Corner: | ||
| − | # What were the early | + | # What were the early traditional measuring modes used. Find out from your elders. |
| − | |||
# Who formulates the standards | # Who formulates the standards | ||
Revision as of 08:55, 13 December 2013
| Philosophy of Mathematics |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist.
Concept Map
Error: Mind Map file Mensuration.mm not found
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional Information
Useful websites
1. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/allgcse/bs7act1.pdf
This is a good website for interesting activities on mensuration.
2.For standard measurements : http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/maths/mathsE1.htm
3.For general rules while writing units ://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_System_of_Units#General_rules
4.For teacher reference on dimension. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/163641/dimension
Reference Books
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1. What is Mensuration ?
Learning objectives
- The students learn that mensuration is the branch of Mathematics dealing with measurement of angles, length, area, and volume.
- Students will learn and understand that it is important to know how to measure things.
- The length of the total boundary of a figure is called its perimeter. The Metric unit of perimeter is same as the unit of length - Metre.
- The perimeter of 2D geometrical figures like quadrilaterals can be obtained by calculating the sum of all the sides of the figure.
- The amount of surface covered by an object is called it area. The Metric unit of area is square metre.
- The capacity of an object to hold is called its volume.
- They should develop the ability to calculate the area, perimeter, volume or side of many different figures.
Notes for teachers
Measurement are an important part of our everyday life. Think about your day; you probably made some measurements.Perhaps you checked your weight by stepping on a scale,measuring shoes to fit your feet in the shoe store, or saw measuring up houses when they are doing renovations etc. If you did not feel well, you may have taken your temperature. To make some soup, you added 2 cups of water to a package mix. If you stopped at the Petrol bunk, you watched the petrol pump measure the number of litres of petrol you put in the car. Measurement is an essential part of every aspect of life. The temperature, height, and weight of a patient are measured and recorded.Samples of blood and urine are collected and sent to a laboratory where glucose, pH, urea, and protein are measured by the lab technicians.By learning about measurement, you will develop skills for solving problems.
Activity No # Importance of measurements and calculations - a discussion
- Estimated Time :45 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed : Note book, pen
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process:
- Ask the children to make a list of all activities in different areas of life where measurements play an important role.
- Have a discussion in the classroom regarding importance of measurements and how difficult life would be without measurements.
Developmental Questions:
- Why measure ?
- How do we measure ?
- What are the measuring modes and units seen at the market, Hospital, Chemist laboratories, Gold shop, Tailors, Bakeries, Petrol bunks, water tankers, milk vendors, contractors, kitchen, airport, and so on.?
- Evaluation:
- Why do you think certain measuring standards are needed ?
- Question Corner:
- What were the early traditional measuring modes used. Find out from your elders.
- Who formulates the standards
Concept #2.Informal units of measurements
Learning objectives
- The students understand that informal ways of measurements are a type of measure which uses non-standard units such as hand spans, armlengths, footsteps or pattern blocks to measure length, area, etc.
- They comprehend that estimate and informal measurement are interchangeable terms.
- They realise that informal measurements are not always the same but vary from person to person.
Notes for teachers
- The teacher can ask the students to gather information regarding earlier informal measuring ways from their elders and have an initial discussion in the classroom.
Activity No # 1. Estimating distances
- Estimated Time :1 hour
- Materials/ Resources needed : Sticks, ropes, writing pad, pencil.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- The students should have been introduced to different forms of informal measurements.
- They should have the ability to measure and document their findings accurately.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process:
- The teacher can ask the students to determine the distances of library, principal's room, playground, dining hall, entrance gate from their classroom using various informal measuring methods.
- The children can decide which method to use - whether foot, sticks or ropes.
- The task can be done in groups of 3 children.
- Document and compare the results.
- Discuss regarding the length of distance.
- Reiterate that it is very important to use same measuring modes to facilitate comparisons.
- Developmental Questions:
- Which point would we mark as the point of reference for measuring our classroom.
- Similarly what are the points of reference for other places.
- How do we mark them.
- Which measuring unit have you chosen ?
- How will you document the findings ?
- How can we tabulate our findings on board for comparisons ?
- What would be our report back time ?
- What are our findings ?
- What conclusions can we draw ?
- Evaluation:
- What have we learnt so far about measuring object?
- Question Corner:
- How can we measure curves?
- What are the problems with informal measuring units?
- Can we think of methods to measure so that measures taken by anyone would always be same for a given object or distance.
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #3. Standard units of measurements
Learning objectives
- They should understand that there is no natural unit for the measurement of surfaces. It is necessary to fix upon an artificial unit and that , that artificial unit is a square. To find the area of a surface is to find how many times this measuring unit can be applied to or is contained times in the given figure.
- It is essential for students to have an understanding of the units used to measure .
- The students should understand that no matter what field of science they enter, they will need to take measurements, understand them, communicate them to others, and be able to repeat them. In other words, all have to speak the same basic language.
- The ability to obtain accurate measurements and communicate those measurements is a key requirement for progress.
- These are the seven basic units in the SI system: the kilogram (kg) (mass), the second (s) (time), the Kelvin (K) (temperature), the ampere (A) (electric current), the mole (mol) (amount of a substance), the candela (cd) (luminous intensity), and the meter (m), (distance).
- A unit is any measurement that there is 1 of.
Notes for teachers
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same physical quantity. Any other value of the physical quantity can be expressed as a simple multiple of the unit of measurement.
For example, length is a physical quantity. The metre is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. When we say 10 metres (or 10 m), we actually mean 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre".
The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to this day. Different systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system.
Activity No # Hunting treasure and measuring
- Estimated Time : 1 hour
- Materials/ Resources needed:
- Weighing pan with measures of 1 kg, 500gm, 250gm and 100gm and 50gm.
- Digital scale
- Postal scale.
- Measuring cans of 1 litre, 500ml, 250 ml, 100ml,
- Measuring tape, Ruler.
- Watch or stop clock.
- Paper and pen.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- The students should have been introduced to the concept of formal measurements.
- They should be well versed with standard units and subunits.
- They should know unit conversions.
- They should have the skill of measuring and recording accurately.
- They should be aware that comparisons can be made only between similar measuring units.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process:
- The idea here is to inculde several measuring units for practise.
- Initially instruct the students regarding the activity and its purpose.
- Group students into 3 in each.
- The teacher shall make packets of things as treasure and hide them in the school premises.
- The students shall pick chits containing clues to hunt and find the packets.
- 30 minutes is given to search.
- The students search packets and come back to classroom.
- The packets may contain cloth, ribbons, ropes, water, fruits, ingredients , vegetable , books , juice, stamps,envelops or any such measurable items.
- The students have to quickly decide which measuring mode they are going to use, measure and record their findings.
- They also have to measure the distance at which they found each and record the time taken to search.
- Developmental Questions
- What measuring apps can you see here ?
- Can you list the purpose of each ?
- Evaluation
- Question Corner:
- What are standard the units of length ?
- What are the standard units of weight ?
- How are liquids measured ?
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #4. Scale drawing
Learning objectives
- The students should comprehend that a Scale drawing is a drawing that shows a real object with accurate sizes except they have all been reduced or enlarged by a certain amount (called the scale).
- Since it is not always possible to draw on paper the actual size of real-life objects such as the real size of a car, an airplane, we need scale drawings to represent the size.
- Drawing to scale is a tool that Engineers use for many different tasks. One key part of every scale drawing is the scaling factor. This number represents the degree to which our scale drawing or scale model has been reduced in size when compared to the original.
Notes for teachers
Activity No # Estimating Tile costs
- Estimated Time :45 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed:
Graph sheets, scale, pencil,
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- The students should have knowledge about scale drawing.
- They should know about scale factor.
- They should understand that a scaling factor should be maintaining as constant throughout the sketches.
- Students should be able to read and understand a scaling factor.
- They should be able to find a scaling factor and create a scale drawing.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process:
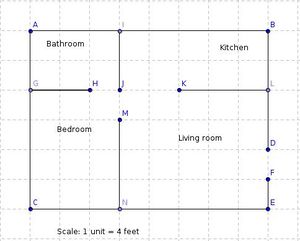
- In the above blue print each individual unit is 4 feet.
- Each ceramic tile costs Rs 80 per square foot.
- How much would it cost to tile the bathroom ?
- How much would it cost to tile Kitchen, Living room and bedroom?
- Developmental Questions
- Along with knowing the length and width of the scale model, what additional information do you need to know ?
- What is the scale factor here.
- Evaluation:
- What are the actual dimensions of each room ?
- Question Corner:
- What all factors do you need to know to estimate the painting costs for each of the rooms.
- How would you go about the calculations.
Hints for difficult problems
Project Ideas
Math Fun
Usage
Create a new page and type {{subst:Math-Content}} to use this template