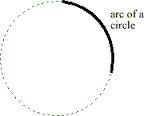
Sector of a circle
| Philosophy of Mathematics |
While creating a resource page, please click here for a resource creation checklist.
Concept Map
Error: Mind Map file CIRCLES BASIC TERMS..mm not found
>
Textbook
To add textbook links, please follow these instructions to: (Click to create the subpage)
Additional Information
Useful websites
Reference Books
Teaching Outlines
Concept #1 CIRCLE CENTRE
DEFINITION: The fixed point in the circle is called centre.
Learning objectives
- Define circle
- give examples for circles
- Locate centre for the given circle.
Notes for teachers
Define circle and centre with the help of a diagram
Activity No # 1 To locate centres for circles
- Estimated Time
20 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed
For the teacher: chalk piece, geometry set.
for the student: paper
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
Instructions for the teacher: Draw few circles of different radii and name the centres
Instructions for the student : name the centres of different circles
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
Identify the centre.
- Evaluation
- How many centres does a circle has?
- Where does the centre of the circle lie? (inside/outside)
- Question Corner
Is there a circle with 3/4/5 centres?
Activity No # 2
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #2 Radius and Diameter
DEFINITION:
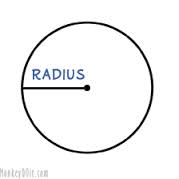
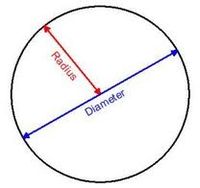
RADIUS:A straight line drawn from centre to the circumference
DIAMETER:A straight line drawn through the centre and terminated both ways by the circumference.
Learning objectives
to draw circle
to draw a diamter
use of geometrical instruments
Notes for teachers
explain the concepts using requisite diagrams. Conduct this activity.
Activity No #1
- Estimated Time
20 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed
different coloured circular cutouts
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- The student should have knowledge of circles.
- The student should have skill of paper folding
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
instructions to the teacher:
The teacher distributes the papeAre the students standing on the circumference of the circle considered to be in the interior or in the exterior ? Justify.r cut outs to all the students.
Ask every student to make 2 equal parts by folding.
What happens if it is folded again to get equal parts?
Ask the students to identify the folded lines/marks
instructions to the student:
fold the paper cut out as per instructions
observe and mark the folded line.
Identity the diameter and radius.
- Evaluation
- Was the student successful in marking radius and diamter?
- Was the student successful in folding and marking?
- Was the student able to relate radius and diameter.
- Question Corner
how many such radii and diameters can be drawn to a given circle?
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #3 CIRCUMFERENCE
DEFINITION: The bounding line of the circle is called circumference
Learning objectives
The student needs to understand that the circumference is the outer boundary of a circle.
Notes for teachers
Explain that every point on the circumference is at equidistant from the centre.
Activity No #1
- Estimated Time
10 minutes.
- Materials/ Resources needed
white paper , compass and colour pencils.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
The student should know to use the compass.
The student should understand the circumference as outer boundary.
- Multimedia resources
Geogebra
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
Instructions to the teachers
Ask the children to draw circles.
Instructions for the students
Colour circumference by fitting small colour pencil in compass itself.
- Evaluation
Observe for the skill in using compass and drawing the circle.
- Question Corner
Is the distance between centre of the circle and its circumference constant ?
What is the distance between the center of a circle and its circumference called?
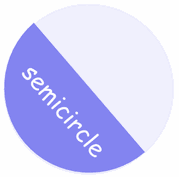
Concept #4 SEMICIRCLE
DEFINITION: PART OF A CIRCLE BOUNDED BY DIAMETER AND THE PART OF A CIRCUMFERENCE CUT OFF BY THE DIAMETER
Learning objectives
- The student should be able to understand that a diameter divides the circle into two equal halves and each such half is a semicircle or hemicircle.
- The student learns how to form a semicircle by joining any two points on the circumference through its centre .
Notes for teachers
Show children the forming of semicircle by drawing diameter.
Activity No # 1
Bring cut circles of different sizes, fold them into exact halves and help them recognise semicircles. Let them colour each half with different colour.
Sub units of activities:
This is a classroom individual activity.
Materials:
White paper, crayons.
- Estimated Time
15 minutes.
- Materials/ Resources needed
White paper, crayons.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
The students should have prior knowledge of circle and diameter.
- Multimedia resources
Geogebra
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
Instructions to the teacher: Ask children the previous day to cut circles of given radius and bring.
Instructions to the students: Instruct them to fold circle into exact half. Draw diameter on folded line and colour each half with different colour.
- Evaluation
Were the students able to draw and cut perfect circles?
Was the folded line (diameter) passing through the center of circle?
- Question Corner
In how many different ways can you draw semicircles for a given circle?
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #5 Interior and Exterior of a circle
DEFINITION:
INTERIOR:The set of all points of its plane whose distance from its centre is less than the length of its radius
EXTERIOR:The set of all points of its plane whose distance from its centre is greater than the length of its radius
Learning objectives
The student needs to understand that any points on the planar surface of the circle within its circumference are said to be interior points and points on the outside of circumference are said to be its exterior points.
Notes for teachers
This knowledge is important to understand secant and tangent to the circle.
Activity No #1
'A game of tiger and goat.'
Draw a circle on the playground. Make children stand on its circumference. Call one student inside the circle to be a goat and other student on the exterior would be the tiger. The tiger tries to get into the circle interior to catch the goat. All other students on the circumference defend the entry of tiger . If tiger forces itself inside, the goat is let out . If the tiger succeeds in catching the goat , the student enacting goat becomes out. Next two more students come forward to be the next goat and tiger and hence the game continues.
Sub units of activity:
This is an outdoor group activity
Instructions to the teachers:
Let this be a fun filled activity and during the game use the terms circle, circumference, interior and exterior.
Instructions to the students:
Identify who is in the interior of circle and who is in the exterior.
- Estimated Time
30mins
- Materials/ Resources needed
A meter length wool nailed to ground (to be centre of circle) and tied to stick on the other side to help draw a perfect circle.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
The students need to know that the circumference of the circle is its boundary and understand the terms interior and exterior of the circle.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
Guage if the students have understood the meaning of the terms interior and exterior.
- Question Corner
Are the students standing on the circumference of the circle considered to be in the interior or in the exterior ? Justify.
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
30 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed
A meter length wool nailed to ground (to be centre of circle) and tied to stick on the other side to help draw a perfect circle.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
The students need to know that the circumference of the circle is its boundary and understand the terms interior and exterior of the circle.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
Instructions to the teachers:
Let this be a fun filled activity and during the game use the terms circle, circumference, interior and exterior.
Instructions to the students:
Identify who is in the interior of circle and who is in the exterior.
- Evaluation
Guage if the students have understood the meaning of the terms interior and exterior.
- Question Corner
Are the students standing on the circumference of the circle considered to be in the interior or in the exterior ? Justify.
Concept #6 Chord
DEFINITION: line joining any two points on the circumference
Learning objectives
- The students should understand that the chord is a line segment joining any two distinct points on the circle
- The students should understand that the longest chord in any circle is its diameter.
Notes for teachers
- Explain the concept by drawing chords of different sizes.
- Make the students understand that the length of the chord increases as it moves closer to the centre and decreases as it moves away from the center.
Activity No # 1
Fold the cut-circular paper at different points. Draw folded lines with different coloured pencils and observe the length of chords.
- Estimated Time :20 minutes.
- Materials/ Resources needed
Circles cut from white paper, colour pencils, scale.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
The students should have the knowledge of circle, diameter, circumference and line segment.
Instructions to the teacher:
Instruct the children to get cut circles ready:
Instructions to the children:
Fold the circle at different points and try to form the smallest and biggest chords.
- Multimedia resources:Geogebra
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
Observe to see if the children are able to fold and mark the chord accurately.
- Question Corner
Name the chord that passes through the center of the circle.
What happens to the length of the chord as it moves away from the centre?
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #7 ARC
DEFINITION: part of a circumference of a circle
Learning objectives
- The students should understand that an arc is a slice of a circle included between two radii of the circle.
- The students should understand the two types of arcs -minor arc and major arc. The larger arc is called a major arc and the smaller one is called minor arc.
Notes for teachers
Explain the concept of arc by drawing a circle and two radii within it. The part of the circle enclosed within and outside the two radii are called its arcs.
Activity No # 1
Get a circular chapati. Cut out a slice by marking its radii and depict major and minor arcs.
This is a classroom individual activity.
- Estimated Time : 10 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed
Chapatis, scissors and scale.
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
The students should have prior knowledge of circle, circumference, radius and line segment.
Instructions to the teacher:
Instruct the children previous day to get circular chapatis.
Instruct them to mark the center of circle by folding it twice over.
Instructions to the students:
Roll chapatis and cut using circular lids to get exact circle shape.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
Were the chapatis exact in circle shape.
Could the students mark its centre, radii and identify the major and minor arcs.
- Question Corner
What is the longest arc of a circle which forms the circle called?
Can you distinguish major and minor arcs when the two radii involved are at 180 degrees.
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #8 concentric circles
DEFINITION:Circles with same centre and different radii
Learning objectives
Notes for teachers
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #9 Congruent circles
DEFINITION: CIRCLES WITH SAME RADII AND DIFFERENT CENTRES
Learning objectives
the student should know the definition of congruent circles
Notes for teachers
Activity No # 1
- Estimated Time
3+10 minutes
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
The student should aware of
- drawing a circle
- defining circle
- defining congruent circles.
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Ask the students to watch the youtube clip
- Was the compass used here?
- what types of circles did he cut?
- Evaluation
- Were the student able to conclude that there are alternatives for compass?
- Can you suggest some more methods of getting a circle?
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Concept #10
Learning objectives
Notes for teachers
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Activity No #
- Estimated Time
- Materials/ Resources needed
- Prerequisites/Instructions, if any
- Multimedia resources
- Website interactives/ links/ / Geogebra Applets
- Process/ Developmental Questions
- Evaluation
- Question Corner
Hints for difficult problems
Project Ideas
- Collect different types of circular objects
- Collect different PIE CHARTS.
- Collect different photographs of tools of cutting circles
- Collect different coins of circular shape
- Collect different images of medals
Math Fun
Usage
Create a new page and type {{subst:Math-Content}} to use this template