Difference between revisions of "Properties of Matter"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[http://www.angelfire.com/mo/matter/General Properties of matter]<br> | [http://www.angelfire.com/mo/matter/General Properties of matter]<br> | ||
[http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_intro.html States of matter]<br> | [http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_intro.html States of matter]<br> | ||
| − | [http://www2.mcdaniel.edu/Graduate/TI/pages/LEWIS/matterweb.htm Matter and its states | + | [http://www2.mcdaniel.edu/Graduate/TI/pages/LEWIS/matterweb.htm Other link about Matter and its states] |
==Concepts== | ==Concepts== | ||
Revision as of 04:36, 4 June 2014
Chapter-8
PROPERTIES OF MATTER
Class-6
OBJECTIVES
1. Students will be able to know about matter
2. Students will identify the properties of matter
3. Students will be able to differentiate the matter based on the property.
4. Students will be able to know characterise the matter.
5. Students will know about mallability and ductility.
6. Students will reason out the usage of metals in jewellery.
7. Students will be able to identify in their surroundings
Useful Weblinks
Properties of matter
States of matter
Other link about Matter and its states
Concepts
a) Matter b) Elasticity c) Stress and strain d) Malleability e) Ductility
Defination of Mass.
Mass corresponds to an idea of how much matter there is in an object.
mass is the ammount of matter that something has
matter is how much of something that something has
Defination of Matter Matter is the substance of which physical objects are composed,
Matter is any substance made of particles with mass. Matter refers to anything that has mass and takes up space - doesn't refer to any amount Objects that take up space and have mass are called matter. Everything around you is made up of matter. Chocolate cake is made up of matter. You are made of matter. Mass refers to "how much" stuff there is - Ex. 1 gram of suga
Activity.1.
Students will list out the objects Around us .
Activity 2.
Teacher will explain categorise the objects based on shape size and structure through the following questions Differnciate the collected objects according to their colours,texture, hardness,occupation in containers
Activity 3.
Teacher will guide the students to catogorise collected object in three categories
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gaseous
Activity 4.
Teacher shows the arrangement of particals in solid ,Liquid and Gaseous state through diagram with explanation.
LINK States-of-Matter States of matter and partical arrangement in three states can be viewed.Differentation of three states explained clearly.
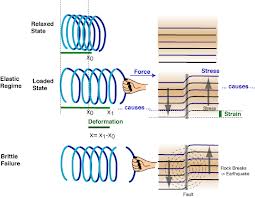
Elasticity.
Activity 1.
Each Students will be given rubber band and tell them to streach it and slowly release the force and Record the observations . On their observation Teacher will Explain the property of matter i.e Elastacity. Atoms in the rubber band are displaced from their equillibrium position. When streach is stoped energy stored in them bring the atom back to the original position.
Teacher will explain, what is atom, displacement and equllibrium
Image acknowledged from the web site Google Images
[en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rubber_elasticity Elasticity]
(Elasticity of some matter is explained with reason in the above wikipidia)
Displacement
The difference between the initial position of something (as a body or geometric figure) and any later position is called displacement. Equllibrium
The state of a body or physical system at rest or in unaccelerated motion in which the resultant of all forces acting on it is zero and the sum of all torques about any axis is zero.
When a body is deformed by the application of external forces are brought play with in the body tending to countereact the external forces
[en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stress–strain_curve Stress-Strain Curve] ( Elasticity stress and strain and more information will be available in above web address)
Hooke's law —
A law stating that the strain in a solid is proportional to the applied stress within the elastic limit of that solid.
first stated formally by Robert Hooke (1635-1703) of England in The True Theory of Elasticity or Springiness (1676).
[www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/271336/Hookes-l Hooke's-Law] wikipedia/wiki/hook's law More Hook's law's and activity can be viewed along with image.
Malleability Activity 1 Students will collect some thin shining sheets which covers the sweet
Activity 2.
Students are asked to visit Blacksmith's work shop and guide them to Report what they observed .
Teacher should explain Malleability of a Metal
Definition: It is one of the property of the metal(matter) that can be obtaine in the form of thin sheets

Ductility
Activity 1. Instruct the Students to collect Metal Threads of different Electric wires
Activity 2. Visit to a nearest Jewellery shop ,observe and List out Thread like Ornaments.
Teacher should explain the Ductible property of Metal.
This resouce is prepared by G.DMahadevanaika mahadevanaika123@gmail.com K.C. Suresh sureshdiet@gmail.com